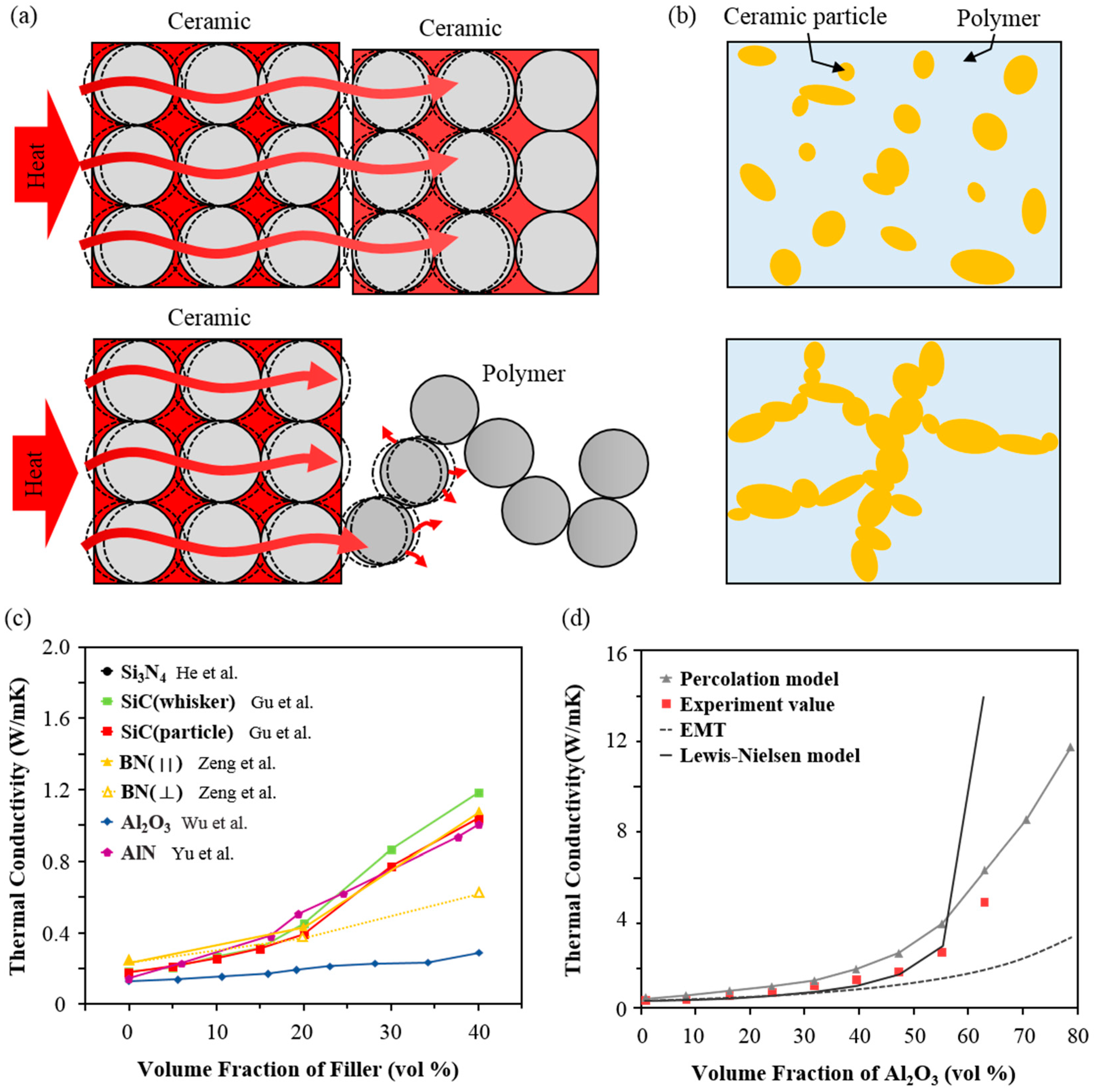
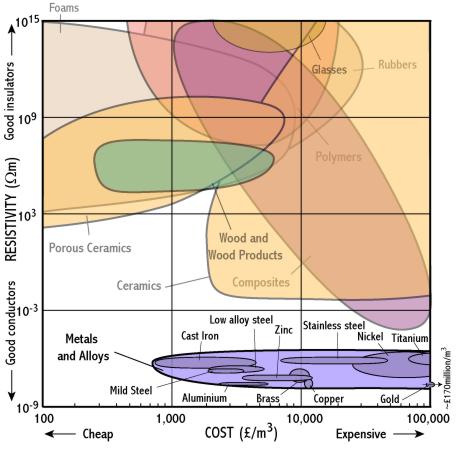
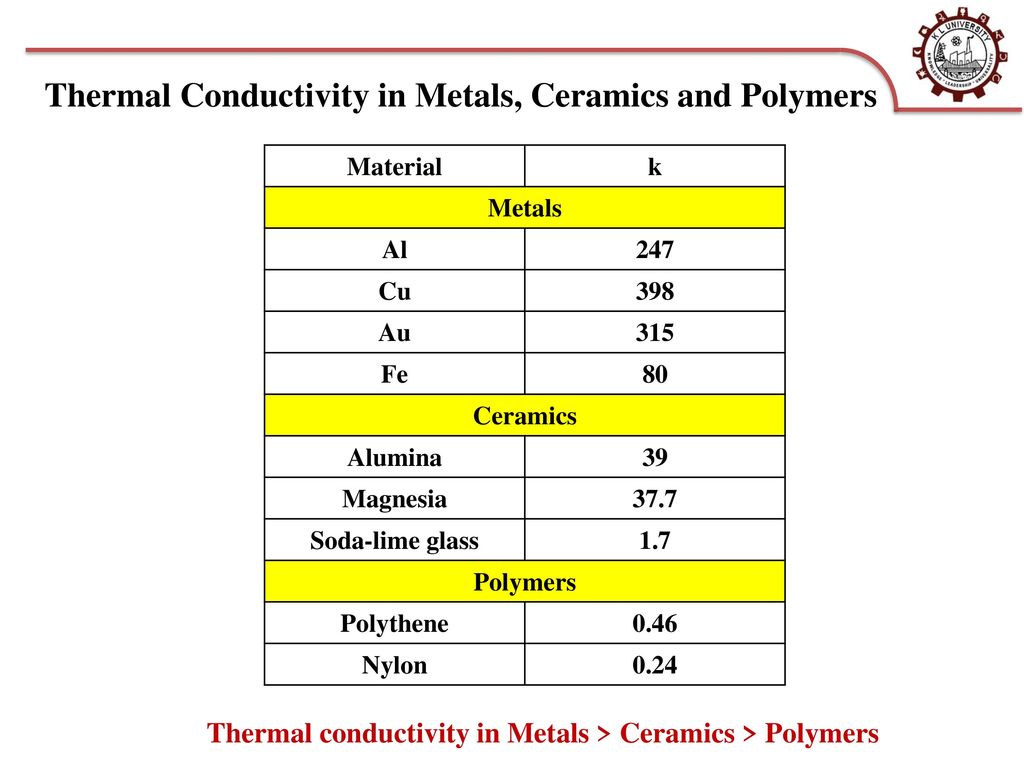
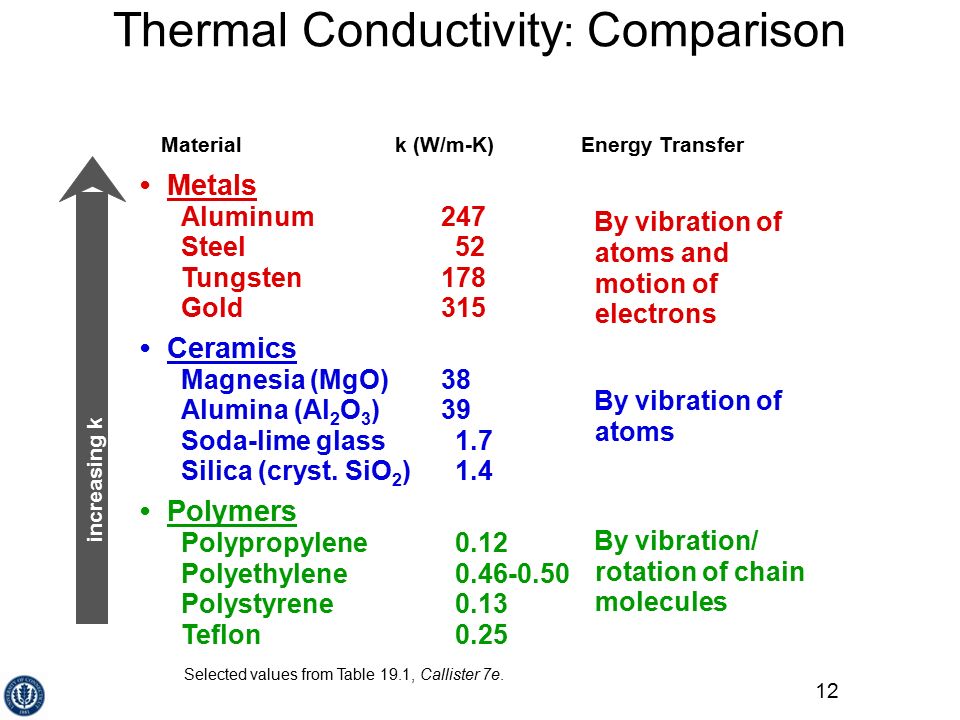
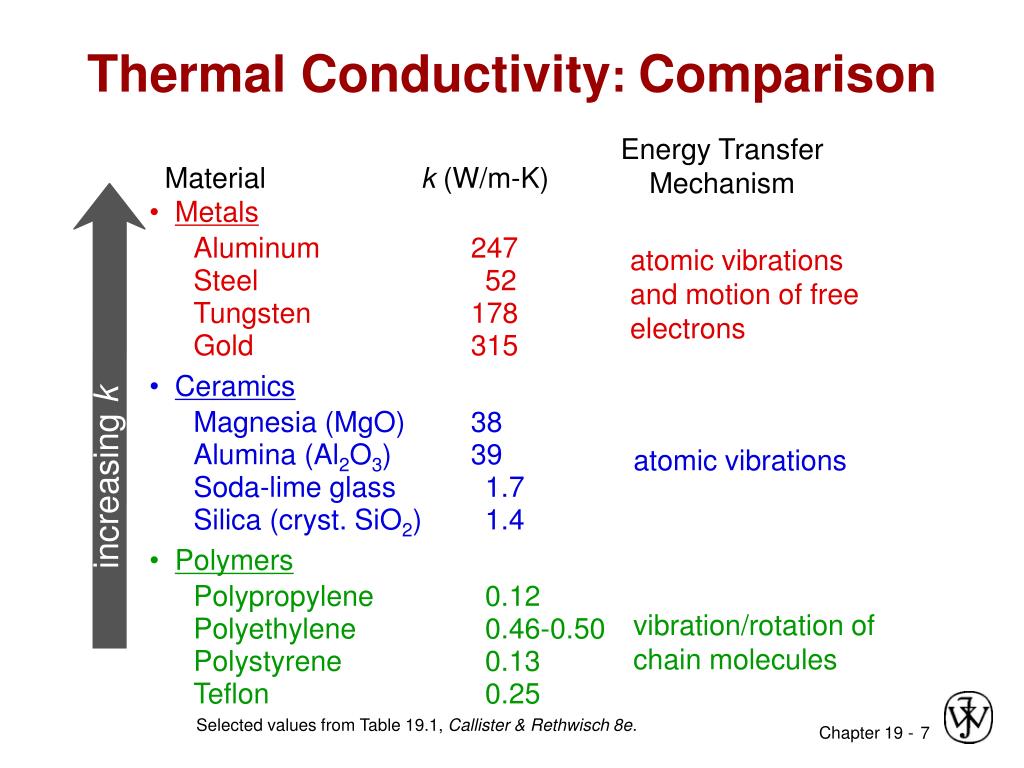
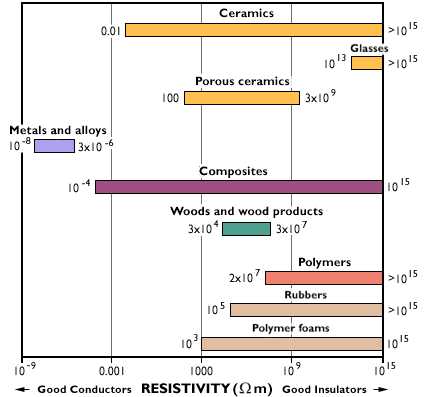
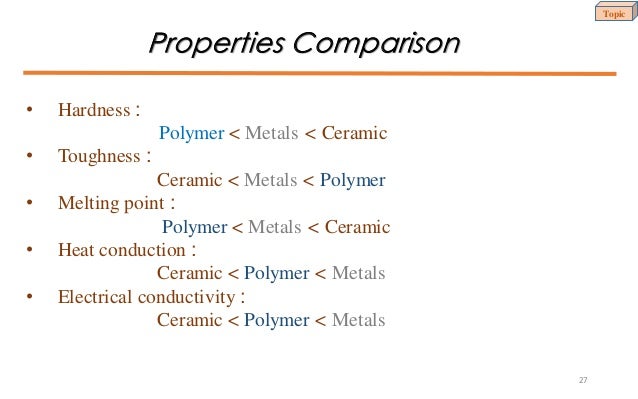
Thermal Conductivity Metals Ceramics Polymers

Generic limestone r is relatively pure polycrystaline calcite solidity is the quotient of the solid grain volume divided by the bulk volume and k is thermal conductivity in w m 1 k 1.
Thermal conductivity metals ceramics polymers. Thermal conductivity k is used in the fourier s equation. Is a measure of a materials ability to pass heat through it. The ratio for the low conductivity polymers is about 0 44 while that for somewhat more conductive glasses and ceramics in 0 80. Compare metals polymers and ceramics on a chart or table using the following properties and the ratings low high and highest.
Increasing thermal conductivity the team is now looking at making composites that combine the new technique with several other heat dissipating strategies to further increase thermal. Many new combinations include ceramic fibers in metal or polymer matrix. This study describes a new method for the measurement of the thermal conductivity of insulating materials in the range from 0 1 to 1 5 w c 1 m 1 which generally covers polymers ceramics and. Tions as seen in their ratio is greater for low thermal conductivity materials like polystyrene and polytetrafluoroethylene than for the higher conductivity materials such as ceramic and glasses.
However bulk polymers usually have low thermal conductivity 0 1 0 3 wm 1 k 1 due to the presence of defects such as polymer chain ends entanglement random. Availability of these polymers can expand the plastics industry by partially replacing metals and ceramics in heat transfer devices and systems leading to energy and cost savings. Calculate conductive heat transfer. Density ductility hardness corrosion resistance hardness thermal conductivity electrical conductivity wear resistance.
Asked jul 25 2020. While heat flow in materials is often a complex process even small improvements in the thermal conductivities of polymers can have a large technological impact. Materials with a high thermal conductivity can effectively transfer heat and readily take up heat from their environment. Poor thermal conductors resist heat flow and obtain heat slowly from their surroundings.
Thermal conductivity k is the quantity of heat transmitted due to an unit temperature gradient in unit time under steady conditions in a direction normal to a surface of the unit area. Lowest thermal conductivity of any pure metal marble.