Thermal Noise Floor Lte
Thermal noise power and voltage equation.
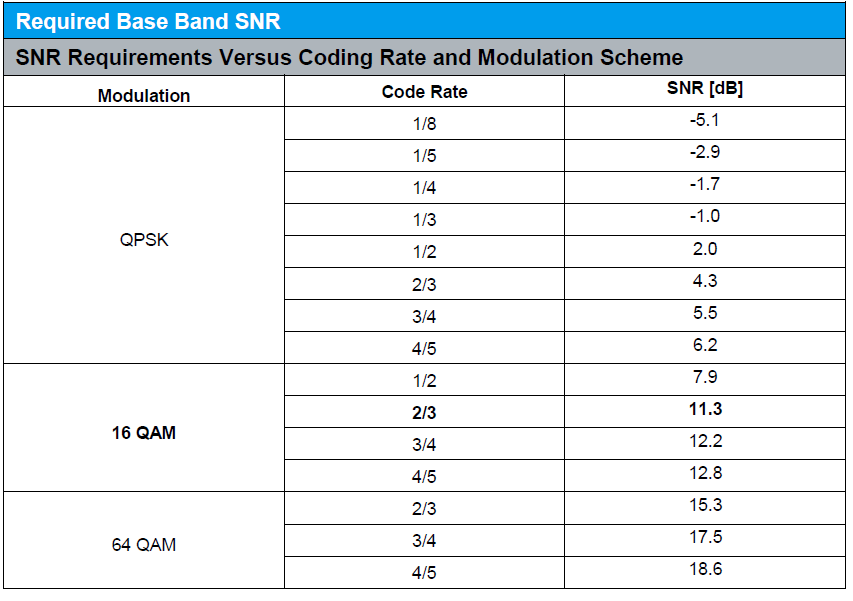
Thermal noise floor lte. It is assumed that the enode b receiver has a noise figure of 2 0 db and the required signal to noise and interference ratio sinr has been taken from link level simulations performed in 1. It can alternately be defined as a signal that produces a signal to noise ratio of a given value m at the output. Basic thermal noise calculation and equations. Thermal noise is approximately white meaning that its power spectral density is nearly equal throughout the frequency spectrum.
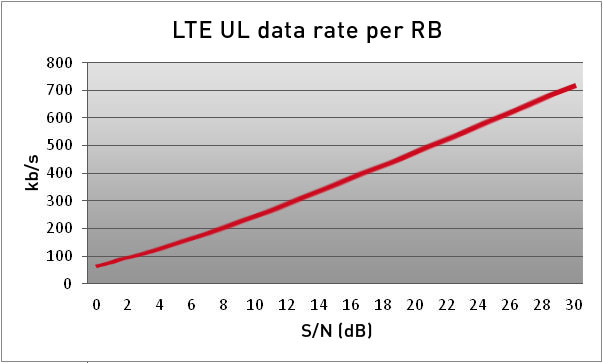
For an analog fm land mobile radio system using 25 khz channels the receiver must have approximately 4 db more signal power than noise power. The background electromagnetic noise over a bandwidth of 10 mhz an entire lte block of ofdm carriers is calculated with the following formula. A minimum detectable signal is a signal at the input of a system whose power allows it to be detected over the background electronic noise of the detector system. Noise power in dbm 174 10 log10 bandwidth in hertz 104 dbm.
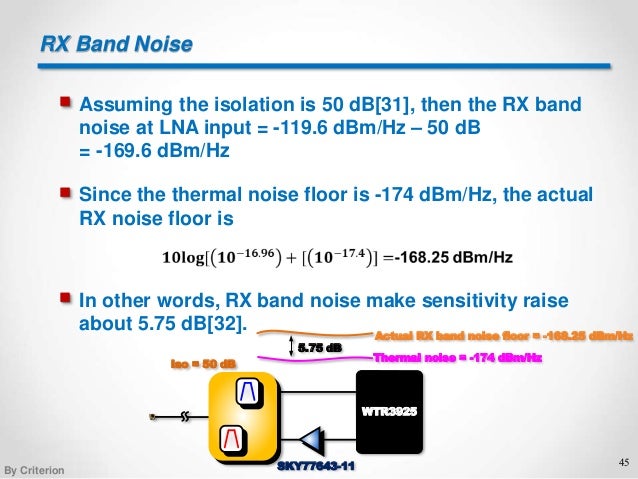
Thermal noise is effectively white noise and extends over a very wide spectrum. Thermal noise spectrum is gaussian in shape. Figure 2 noise figure added to thermal noise ktb. Often a site link budget maximum range is used to evaluate the process.
The required ratio of signal power to noise floor is known for certain types of modulation. This represents a carrier to noise ratio 4 db. The ue terminal power is assumed to be 24 dbm without any body loss for a data connection. Noise figure nf is a measure of degradation of the signal to noise ratio snr caused by components in a signal chain.
Following equation or formula is used for thermal noise power and voltage calculator. Thermal noise in a 50 ω system at room temperature is 174 dbm hz. This is an online calculator that calculates thermal noise power based on temperature and bandwidth. Everything rf has the largest selection of online calculators for the rf and microwave industry.
The noise resulting from thermal agitation of electrons is referred as thermal noise. In some literature the name sensitivity is used for this. To calculate the thermal noise levels there are formulas or equations that are relatively straightforward. In other words the system is interference limited as opposed to limit noise.
Margin sites intrusive noise levels due to an increase can be considered as if sites were spaced closer together than position using the same frequency the thermal noise floor. An interference margin of 2 0 db is assumed. Just enter the value and click calculate. In addition to this there is an online calculator to provide additional assistance.
This example shows how cabinet radiation could potentially interfere with wireless reception of low level signals.