Types Of Bonding Structure Of Ceramic Materials

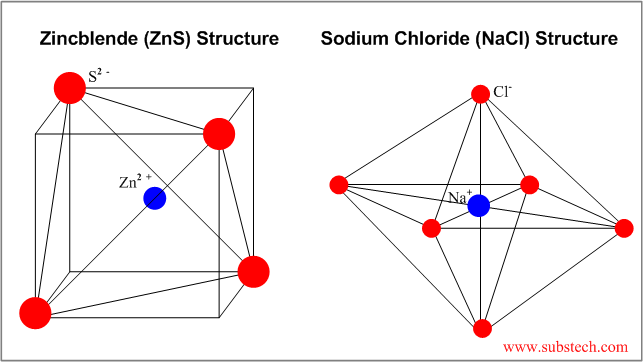
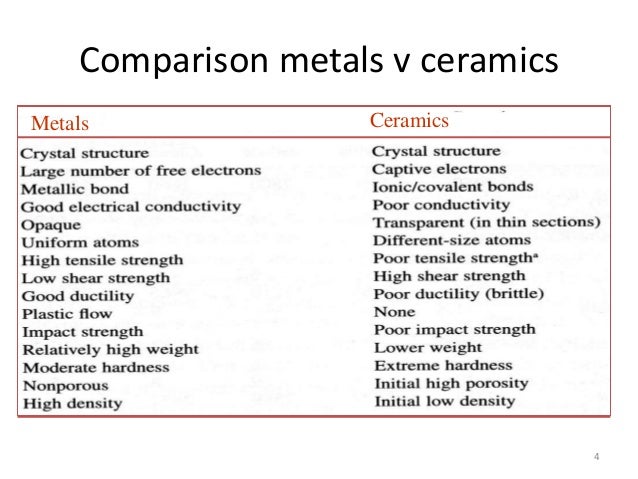
Although both types of bonds occur between atoms in ceramic materials in most of them particularly the oxides the ionic bond is predominant.
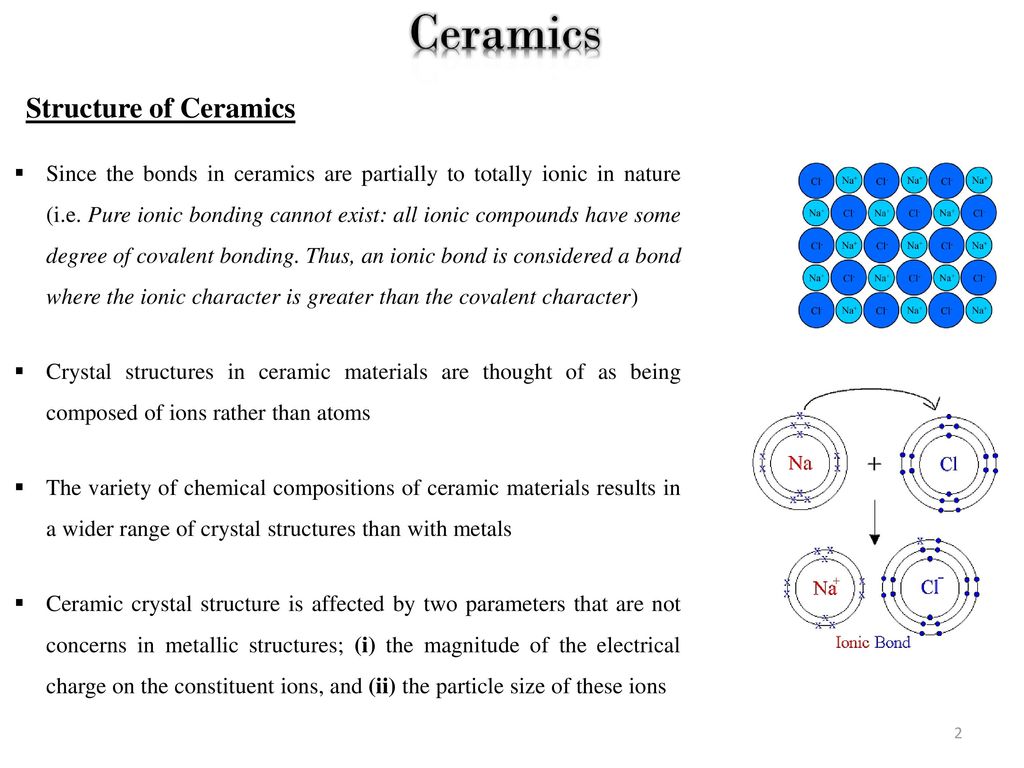
Types of bonding structure of ceramic materials. As we study materials in further detail in this course we will utilize these associations to explain observed materials properties in the different. In ionic bonding a metal atom donates electrons and a nonmetal atom accepts electrons. Most ceramics are made up of two or more elements. Covalent bonding instead occurs between two nonmetals in other words two atoms that have similar electronegativity and involves the sharing of electron pairs between the two atoms.
Usually they are metal oxides that is compounds of metallic elements and oxygen but many ceramics. Michael pfeifer in materials enabled designs 2009. Recall that the predominant bonding for ceramic materials is ionic bonding. The properties of ceramic materials like all materials are dictated by the types of atoms present the types of bonding between the atoms and the way the atoms are packed together.
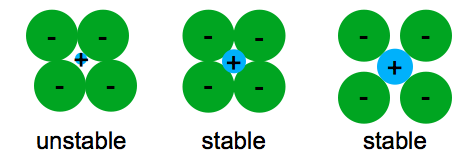
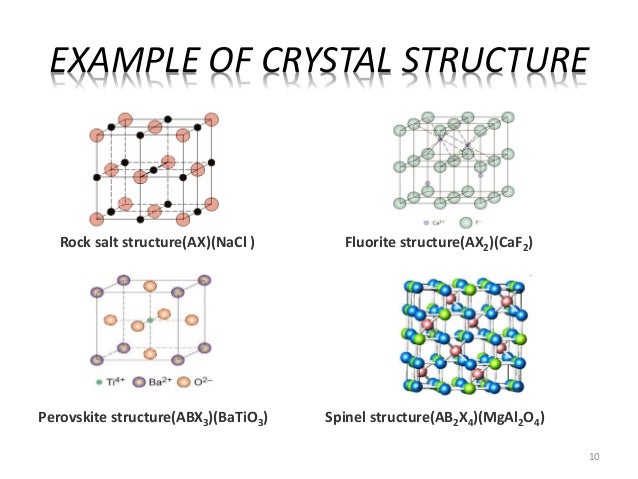
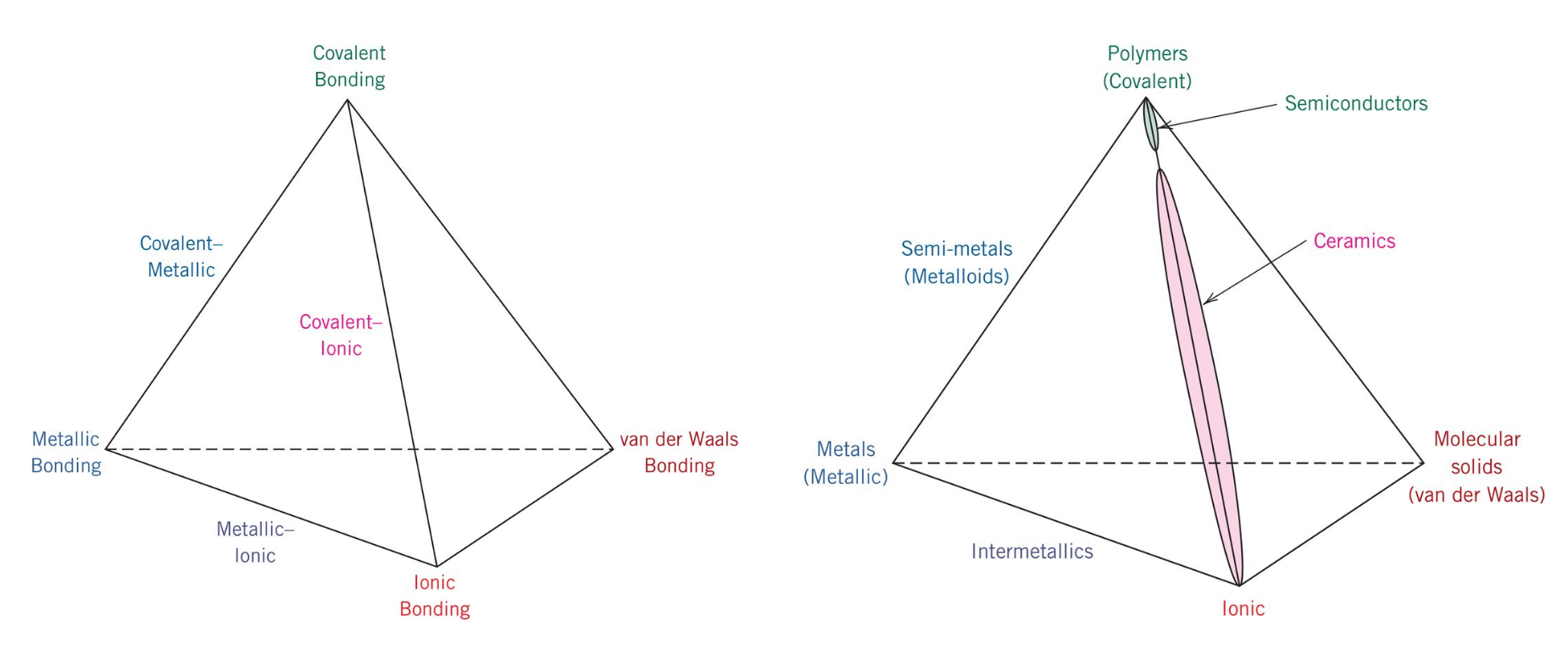
The bonding structure and crystal structure within a ceramic material are fundamental physical features that determine the intrinsic physical mechanical thermal electronic and magnetic properties of a given ceramic. Ionic bonding is associated with ceramics covalent bonding is associated with polymers metallic bonding is associated with metals and van der waals bonding is associated with molecular solids. The atomic bonding and crystal structure in ceramics are determined. What is a ceramic.
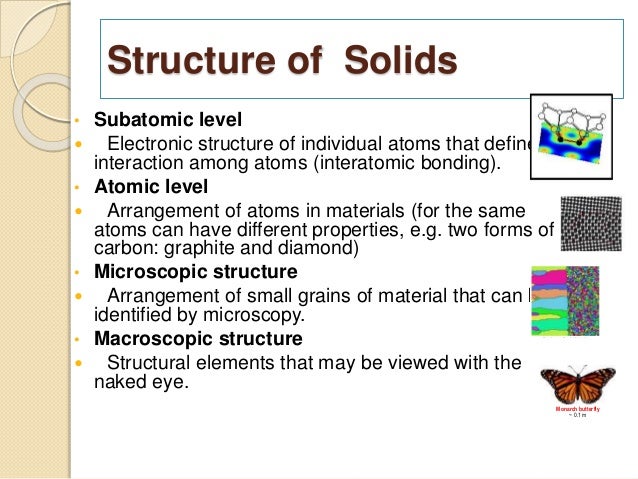
This is known as the atomic scale structure. 4 5 2 atomic bonding and crystal structure in ceramics.