Upper Floor Of Peritoneal Cavity
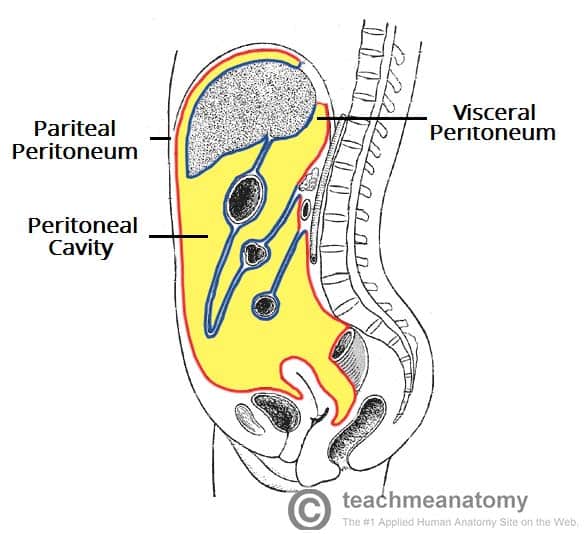
The peritoneum consists of two layers.
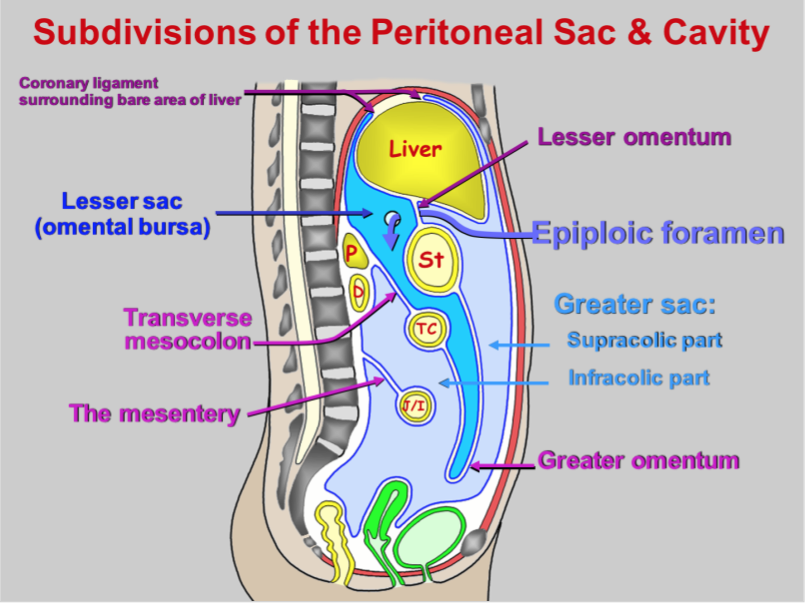
Upper floor of peritoneal cavity. Lesseer sac greater sac lesseer sac omental bursa also c d omental bursa or left subhepatic space or left posterior intraperitoneal space. It forms the floor of the lesser peritoneal sac. The abdominal cavity the space bounded by the vertebrae abdominal muscles diaphragm and pelvic floor is different from the intraperitoneal space located within the abdominal cavity. Its upper boundary is the diaphragm a sheet of muscle and connective tissue that separates it from the chest cavity.
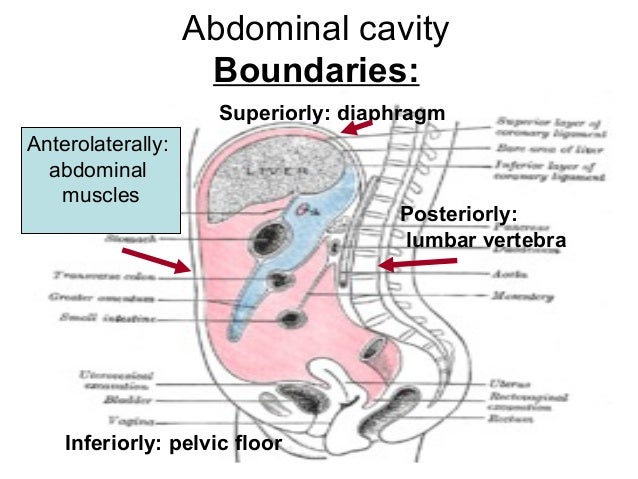
This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels lymphatic vessels and nerves. The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is composed of muscle fibers of the levator ani the coccygeus muscle and associated connective tissue which span the area underneath the pelvis the pelvic diaphragm is a muscular partition formed by the levatores ani and coccygei with which may be included the parietal pelvic fascia on their upper and lower aspects. Vertically it is enclosed by the vertebral column and the abdominal and other muscles. Content of peritoneum doesn t spread into upper storey of the abdominal cavity through its lateral canal.
Its lower boundary is the upper plane of the pelvic cavity. Olof heimbürger md phd in chronic kidney disease dialysis and transplantation fourth edition 2019. Parietal peritoneum an outer layer which adheres to the anterior and posterior abdominal walls. Duodenojejunal junction is located in the left upper quadrant.
It is suspended by the suspensory muscle ligament of the duodenum. An intraperitoneal recess that lies posterior to the stomach and lesser omentum. Lesser sac omental bursa. Peritoneal cavity is the potential space b w parietal visceral layers is filled with serous peritoneal fluid.
Envelops all intraperitoneal organs. It normally contains only a thin film of peritoneal fluid which consists of water electrolytes leukocytes and antibodies. The main peritoneal cavity. Space potential between the parietal and visceral peritoneum.
Extends from the diaphragm to the floor of the pelvis. Although in adults the peritoneum looks like it s scattered all over the place there is a. The peritoneal cavity is the largest serosal cavity in the body with a surface area of approximately 1 to 2 m 2 although the peritoneal area is commonly suggested to be similar to the body surface area recent studies suggest that the anatomical surface area of the. Abdominal cavity largest hollow space of the body.
What structure can be the reason of it. Overview of abdominal viscera alphabetical. Visceral peritoneum an inner layer which lines the abdominal organs. It s made when parietal peritoneum reflects from the abdominal wall to the viscera.
D left flexion of.









:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3052/hVBlhcHNZl1nPG3751Xkfw_Peritoneum_01.png)






:format(jpeg)/images/container/peritoneal-cavity/Peritoneal_cavity_2.png)