Urethral Anatomy Rug Radiology

Although vcug or rug can demonstrate the urethra per se the anatomy of the urethra and adjacent structures can be better evaluated with mr imaging fig 3.
Urethral anatomy rug radiology. A better understanding of urethral anatomy key imaging features distinguishing underlying disease and the imaging appearance of normal urethral postoperative changes will aid radiologists in providing a complete evaluation and accurate diagnosis. Additionally although the bladder is not generally the main target of the exam as with a cystogram a vcug mcu may be useful in the detection of bladder abnormalities and vesicoureteric reflux vur. Female urethra urethral duplication can occur in female patients. Introduction urethrography is most commonly performed via the retrograde injection of radiopaque contrast into the urethra to elucidate urethral pathol.
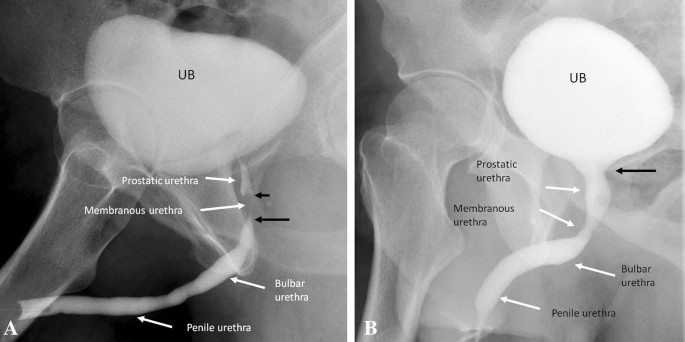
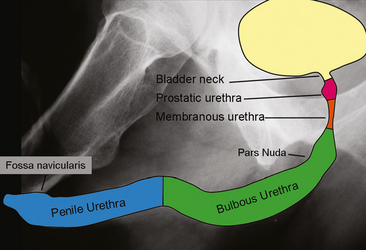
Generally a rug asu is carried out to visualize anterior urethral abnormalities and a vcug mcu for posterior urethral abnormalities. Overview a retrograde urethrogram rug is a diagnostic procedure performed most commonly in male patients to diagnose urethral pathology such as trauma to the urethra or urethral stricture. It commences at the internal urethral orifice in the trigone of the bladder and opens in the navicular fossa of the glans penis at the external urethral meatus which is the narrowest part of the urethra. After viewing this presentation the reader will be more familiar with the core performance of rug and vcug examinations.
Contrast seen entering the urinary bladder.